How the Pseudalert Test works
The Pseudalert Test detects the presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in water samples.The test is based on a bacterial enzyme detection technology that signals the presence of P. aeruginosa through the hydrolysis of a substrate in the Pseudalert reagent. P. aeruginosa cells rapidly grow and reproduce using the rich supply of amino acids, vitamins, and other nutrients present in the Pseudalert reagent. Actively growing strains of P. aeruginosa have an enzyme that cleaves the substrate in the reagent to produce blue fluorescence under ultraviolet light.
Pseudalert detects Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 1 cfu per 100 mL water sample within 24 hours.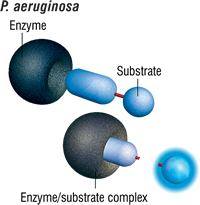



 Add reagent to sample (sample will turn yellow), and then incubate at 38°C±0.5°C for 24–28 hours.
Add reagent to sample (sample will turn yellow), and then incubate at 38°C±0.5°C for 24–28 hours. Read under ultraviolet (UV) light. Blue fluorescence indicates presence of P. aeruginosa. See the
Read under ultraviolet (UV) light. Blue fluorescence indicates presence of P. aeruginosa. See the  Add IDEXX Antifoam Solution to vessel.
Add IDEXX Antifoam Solution to vessel. Pour sample into
Pour sample into  Seal using a
Seal using a  Read under ultraviolet (UV) light. Blue fluorescence indicates the presence ofP. aeruginosa. Count the positive (blue fluorescent) wells and refer to MPN table. See the
Read under ultraviolet (UV) light. Blue fluorescence indicates the presence ofP. aeruginosa. Count the positive (blue fluorescent) wells and refer to MPN table. See the 



